Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus is a chronic condition affecting millions worldwide. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), diabetes prevalence has surged in recent decades, now impacting over 400 million people globally and continuing to rise. In type 2 diabetes, the body either produces insufficient insulin or resists its action, hindering the cellular uptake of blood sugar (glucose). This disruption causes hyperglycemia, a dangerous increase in blood glucose levels. Importantly, diet management is vital for stabilizing blood sugar levels and enhancing overall health in individuals with type 2 diabetes.
In this article we will look into the aspect of diet & type 2 diabetes management moderation, what food should be consumed and what not, as well as those strategies that aim in improving the compliance with the effective dieting. We shall also critically examine the current research findings and statistical data, including competent opinions on dietary management in diabetes mellitus prevention and control.
Understanding the Role of Diet in Type 2 Diabetes Management
When it comes to people enduring type 2 diabetes, food consumption is among the most dominant factors that control the condition. Elevated levels of blood sugar (known medically as glycaemia) can cause dangerous complications such as arterial complications, kidney complications, nerve damage, and even loss of vision. Changes in the diet can reduce blood sugar levels and help alleviate such complications.
The overall weight aspects of dietary control in Type 2 Diabetes are aimed at improving the patient’s sensitivity to insulin and maintaining normal ranges of blood sugar. Also, proper food choice encourages management of weight which is important for diabetic persons. This is because the American Diabetes Association (ADA) believes that one can drastically improve insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control by simply losing about 5-10% of body weight.
Diet controlling is, however, not an uniform treatment regimen for an individual and hence the need for consideration. There is no doubt that food admixtures differ from one person to another, and there are also other aspects like the person’s age, active hours, and other illness which have an influence on how a person eats. For these reasons, it is important to consult a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian before designing a diet that will match the individual’s short term and long term health aspirations.
Essential Guidelines for Nutrition in Diabetes Type 2
Diet therapy for type 2 diabetes is founded on a number of primary principles. These emphasize the importance of balanced meals, the moderation of carbohydrate consumption, the selection of intergral foodstuff with low energy density, and adequates serving sizes. Adhering to these principles has made it easier for the individuals to regulate the levels of glucose in the blood.
1. Manage the intake of Carbohydrates
It is carbohydrates that have the greatest impact on blood sugar levels. Upon consumption of carbs, the body tends to transform these components into glucose (sugar) which is then released in the blood. For diabetic individuals, eating a lot of carbohydrates can cause extremely high glucose levels within a short span of time. Therefore, management of carbohydrates is one of the principles in the diabetes treatment.
Carbohydrates are further divided into two major groups simple and complex. Simple carbs are sugary contents contained in junk foods, candies, and soda pops, these tend to elevate the blood sugar rapidly. Complex carbohydrates in contrast are contained in whole grain cereals, fresh vegetables, and legumes and take a longer time to get absorbed hence gives a more balanced blood glucose distribution.
Diabetes is a very difficult disease to manage without properly controlling carbohydrate consumption. This is achieved by:
- Opting for unprocessed foods such as brown rice, quinoa, and oats. These are healthy foods that have high fiber content and below refined index, and therefore assist in managing blood sugar levels.
- Consuming veggies like leafy greens cup with cucumber tomatoes and capsicum. These are low carbohydrate foods which are high in fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
- Reducing processed sugary foods and grains such as white bread, cakes and sweets. They are high glycemic index foods and lead to a rise in blood sugar and promote resistance to insulin action.
2. Healthy Fats in the Diet
Incorporating fat into a diet designed for diabetes is possible, however, one must be cautious as to the type of fat included. Good types of fats can help control heart diseases which are known complications associate with type 2 diabetes. In fact, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention states that heart failure is the progressing health concern that kills most patients with diabetes. This is the reason why monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats are recommended because they help in optimizing blood lipid profiles and moderating inflammation.
Healthy fats can mostly be sourced from:
- Bottles of olive oil essences where there are high levels of oleic acid and other compounds with antioxidant properties.
- Usage of avocados, which offer users with mono-saturated fat along with other nutrients such as fiber.
- Consumption of nuts such as almond, walnut, and cashew nuts which contain good amounts of healthy fats and fiber too.
- Eating oily varieties of fish rich in omega-3 fats like salmon, mackerel and sardines.
On the other hand, eating trans fats which are found in snack foods and baked products along with saturated fats which found in high-fat meat cuts and whole-fat dairy products should be avoided as much as possible because they enhance the risk of developing heart-related illnesses and also impair the glycemic control.
3. Add Lean Proteins
We all need protein in our diet because apart from building and repairing of body tissues, it works to control blood sugar. Low-fat protein rich foods are more beneficial for people with type two diabetes because such proteins will not add much fat in their calories nor will they spike their blood sugars.
Lean sources of protein include:
- Poultry, especially skinless ones, for instance chicken or turkey.
- Seafood especially oily ones like salmon fish that are high in omega-3 levels.
- Tofu and tempeh, as sources of plant-based protein.
- Dried beans and lentils including kidney beans, chick peas and black beans, which add protein as well as fiber.
Eating lean protein stabilizes blood sugar levels as it tends to slow down the utilization of carbohydrates and eliminate glucose level spikes.
4. Add Foods that Are High in Fiber
Fiber has an important function in regulating blood sugar levels. It slows down the amount of glucose that can enter the blood in order to avoid the increase of blood sugar levels. Fiber is also helpful for helping in controlling weight as it makes one feel satisfied and helps in digestion.
Sources of fiber are:
- Fruits that are found in tropical climates, like apples and pears, berries, citrus fruits, among others.
- Most vegetables, especially those that are low in carbohydrates such as bok choy, carrots, and even cucumbers.
- Whole grains that include oats, quinoa, or even brown rice.
- Lentils, beans, and peas.

The benefits of adding fiber to one’s diet go beyond management of blood sugars as they also promote a healthy digestive system as well as prevent heart problems. The advisable amount for an adult is between 25 and 30, though the figures depend on one’s health requirements.
Foods that You Must Add to Your Menu
Nutrition is important for any patient, but there are foods that are especially useful for a person suffering from second type diabetes. This includes foods that help keep blood sugar in check, give vital nutrients, and encourage healthy living in general. Let us highlight some of the food choices that can be taken in order to better cope with diabetes.
1. Non-Starchy Vegetables
Non-starchy vegetables such, as spinach, kale, celery, broccoli, onion, and bell pepper are high in fiber but mostly contain few calories. Furthermore, these vegetables are not only low calorie but also rich in minerals, vitamins, and antioxidants hence very important for health. In fact, when diabetes patients consume more non-starch vegetables, it has been found that their blood glucose levels are better controlled and the risk of complications arising from diabetes diminishes.
2. Whole Grains
Whole grains that are brown rice, quinoa, barley, whole wheat bread has a high fiber content and nutrients. Whole grains are the digested slower than the refined grains due to their lower glycemic index, which also helps in keeping the blood sugar levels in control. Treated with sustained energy providing carbohydrates, blood sugar levels are easily maintained in check with whole grains as complex carbs energy sources.
3. Lean Proteins
Lean proteins are important for muscle mass development, tissue repair, and keeping blood glucose levels within normal ranges. Choose skinless chicken, fish, tofu, and beans as protein sources. These are healthy protein sources with low fat and easily manageable blood sugar levels.
4. Healthy Fats
The active fats like an avocado, a drizzle of olive oil or nuts can be health promoting and also give sustained energy for a long period and good for the heart. These fats are good enabling sugar control and also minimizing inflammation by making the sugar absorb into the blood quite slower.
5. Low-Fat Dairy Products
Dairy Low-fat products such as milk, yogurt, cheese contain calcium and vitamin D which are important for the health of the bones. These dairy substitutes are low-calorie and low-fat dairy products making them safe for those who have type two diabetes and are on weight control.
6. Fruits in Moderation
Fruits provide many important vitamins and minerals needed in a person’s body. Berries, Apples, and juice also have a good content of fibers and antioxidants making it helpful for diabetic patients. However, when it comes to fruits and diabetes, they contain sugars but also fiber which is great in regulating blood sugar. However moderation is important as some fruits such as bananas and grapes are high glycemic and can cause blood sugar spikes easily.
Foods that Are Not Good or Should Be Limited
There are foods which help in the management of diabetes and there are those which make it more difficult to maintain blood sugar levels. Some foods should be limited or avoided entirely and include the following:
1. Foods and drinks high in sugar
Sweetened or sugar added Products such as games, confections, or baked products contain high refined sugar content and almost negligible if at all a nutritional benefit. Such foods also cause high blood glucose levels within a short period which can further lead to hyperglycemic episodes. Nonetheless, these can exacerbate the chances of insulin resistance and its related complications such as heart attack or even neurological problems. It would therefore be wise to cut down or completely eliminate the consumption of sweetened snacks and beverages with high sugar content, including those containing agave or added sugars like tinned fruit, fruit juices, and sweetened yogurt, and instead utilize natural sweeteners available such as fruits.
2. White-washed or processed food grains with sugar.
High glycemic indexes are associated with refined carbohydrate foods such as white bread, white rice, and refined flour cuts of pasta. In simple terms, they have fast digestion levels which lead to a quick increase in blood sugar levels. Such starches are often low in fiber which would have help in retarding digestion to a certain degree. It is advisable to incorporate non-processed carbohydrates in place of highly refined carbohydrates in the dietary practices of diabetics.
3. Fried and Fatty Foods
Fried foods like french fries, fried chicken, and donuts are filled with unhealthy fats. These increase the bad cholesterol levels (LDL cholesterol) in blood and blood pressure levels also increasing the likelihood of developing heart disease which is often associated with diabetes. Therefore, baked, grilled or steamed foods are the best alternatives for the diet in the management of diabetes.
4. Processed Meats
Meats such as bacon, sausage, hot dogs, and other culinary processed meats are high in salt, bad fat and preservatives. These are associated with the increased risk of hypertension, heart attack, and stroke. Furthermore, epidemiological studies have also found a lot of processed meat consumption to be associated with hyper inflammatory states and insulin resistance, hence not fit for a person suffering from type 2 diabetes.
Meal Planning Avoid Gaining Control for Type 2 Diabetes
The dietary preparation schedule plays a significant role in the treatment of such medical condition as type 2 diabetes. Blood sugar levels are stabilized, and the body is nourished sufficiently through a sound eating plan. Presented below are some handy meal preparation tips that will help people suffering from type 2 diabetes:
Balance Your Plate
People should try to ensure that half of the plate is filled with non-starchy vegetables such as leafy greens, cucumber, and bell pepper. One-fourth of the plate should be occupied by lean protein sources such as meat, fish, or legumes, while the other quarter should be filled with whole-grain products or starchy vegetables such as sweet potatoes. Such proportion control helps avoid battle with overeating as well as maintains proper sugar levels in the blood.
Watch Portion Sizes
Consuming healthy foods in excessively large quantities may also contribute to excessive caloric intake and therefore to weight gain and obesity associated problems with blood sugar control. You may wish to employ the use of measuring cups or even a food scale for assistance in overseeing portion sizes.

Meal Prep
Tomato, beets, onions and other such veggies can be chopped much ahead of time and stored in the fridge as use of pre packaged food might be unhealthy. For instance, doing the meals on a weekend will take less time in the week to hela even the need of opting for healthier yet un alarming take away fast food or even junk food naked meal prep.
Make It A Point To Snack Wisely
Any time there is a thirst for food before a meal, do not eat junk food instead, reach for a healthier option, like a couple of almonds, some carrot sticks or a few spoonfuls of Greek yogurt. These food items prevent blood glucose levels from getting out of control due to their high protein and fiber composition.
Increase Intake Of Water
Endeavor to drink enough water during the day. But rather than drinking sweetened refreshments, especially sodas and even juices, do as much as possible to reduce blood sugar levels in the body. For people who cannot stand drinking plain water, twiddle with adding lemon wedges or cucumber pieces in the water.
Monitor Your Blood Sugar Levels
Maintenance of a dietary as well as a blood glucose levels diary may reveal certain tendencies and explain the effects of various food types on the body. It will also help actuate better food decisions in the subsequent times.
The Place of Physical Exercise in the Life of Diabetics
As stated in the numerous studies conducted on the management of diabetes, it has been found that while nutritional practices play a significant part, the regular engagement in intense physical exercise presents its unique advantages on the management of the disease. Physical exercise enhances the body’s insulin a hormone that is essential in enabling the cells take in glucose in the blood stream. This is also important as physical exercises helps control one’s weight, helps relieve stress and increases the efficiency of the heart all of which are critical to a diabetic patient.
Some of the activities that one may engage in, in order to lead a more active life include the following:
- Aerobic activities such as walking, swimming or cycling are all important in promoting good health by ensuring the heart is healthy and sugar levels in the blood are low.
- Resistance exercises using weights or resistance bands will increase muscle mass and therefore insulin sensitivity.
- Balance and endurance activities like yoga and stretching can foster relaxation and improve health.
It is advisable that one engages in moderate exercise of at least 150 minutes per week and occurs in sessions within in a week. This may also allow better control of your diabetes and consequently enhance your life.
Managing Weight is Beneficial for Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes
Being overweight, especially in the abdominal area, significantly increases the chances of developing insulin resistance. Reducing one’s weight, on the other hand, improves insulin action or the ability of the body to control blood glucose levels. In fact, research has indicated that weight reduction by even 5-10% would greatly enhance blood glucose levels and general health.
Nevertheless, dispelling obesity should be emphasized over short-term crash diets. Using a safe and balanced weight loss program and exercising weekly, an aspiring dieter should strive to lose about 1-2 pounds per week which is more realistic and healthier in the long run.
How Stress Influences Blood Sugar
Blood sugar levels are also prone to stress changes. The production of certain hormones, such as cortisol, increases blood sugar levels, as the stress response is elicited by the body. Prolonged exposure to stress can cause chronically elevated blood sugar levels, which complicates the management of type 2 diabetes. Hence, control of stress is also included in diabetes management.
Some effective ways to address stress are:
- Meditation and concentrating on the breath to relax the head.
- Engaging activities like writing or walking in the park are considered mindful pursuits.
- The availability of family members, friends, or diabetes support groups lessens the burdens of stress and loneliness.
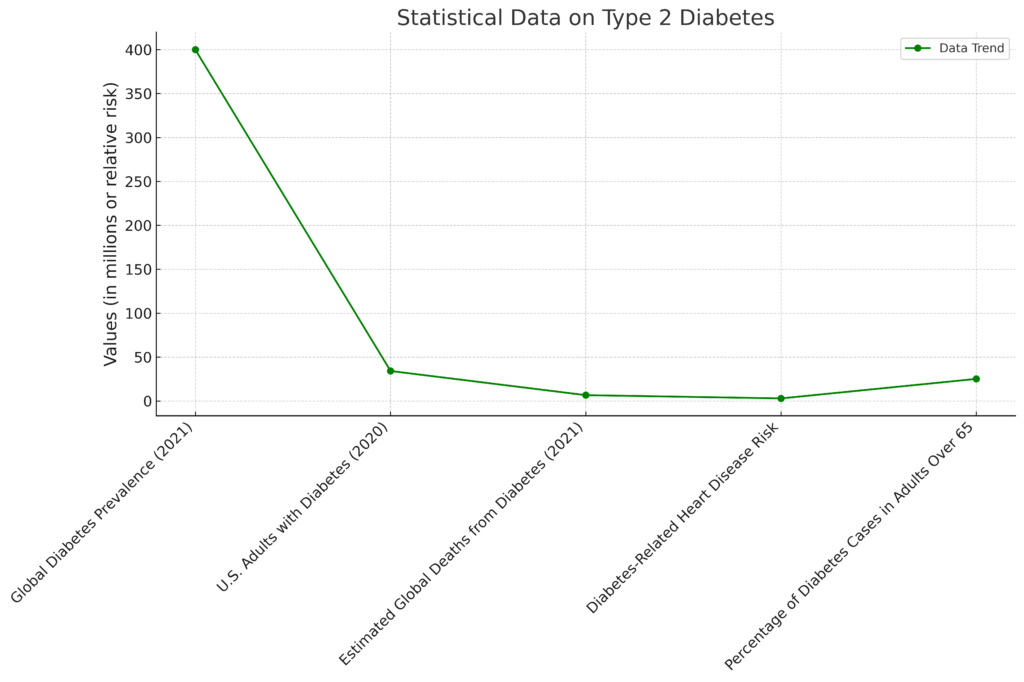
Statistical Data on Type 2 Diabetes
Below are some recent statistics in order to illustrate the prevalence of type 2 diabetes across nations and the need to address the disease appropriately:
| Statistic | Data |
|---|---|
| Global Diabetes Prevalence (2021) | Over 400 million people |
| U.S. Adults with Diabetes (2020) | 1 in 10 adults (about 34.2 million) |
| Estimated Global Deaths from Diabetes (2021) | 6.7 million deaths |
| Diabetes-Related Heart Disease Risk | 2 to 4 times higher than in non-diabetics |
| Percentage of Diabetes Cases in Adults Over 65 | 25.2% of people in this age group are affected |
These statistics emphasize the urgent need for effective diabetes management strategies, including dietary interventions that can make a significant difference in controlling blood sugar and preventing complications.
Conclusion
Dietary measures for the control of type 2 diabetes do not merely entail elimination of certain types of food. It is about choosing foods that promote good health and provide an improvement in blood sugar levels over time. For instance, adding more whole grains, lean protein, healthy fats, and fiber rich foods to your diet will help better control your blood sugar levels. Physical activity, portion sizes, as well as having meals in an attentive manner, are also important in working towards appropriate body weight and preserving the function of insulin.
There is no perfect regime for managing Type II diabetes. Nevertheless, those principles will allow you to develop an appropriate dietary regimen for yourself. Do also remember that those recommendations should be personalized by contacting your doctor. You can manage diabetes and enjoy the fullness of life thanks to an active lifestyle that conquers health challenges.
Read more about Health Performance: Boost with Nutrition and Exercise
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is Type 2 Diabetes?
Diabetes Melitus type 2 is a metabolic disorder that develops when the body does not make enough insulin or when the body’s cells do not respond to insulin produced sufficiently, causing an abnormal increase in blood glucose levels. It can cause a host of illnesses such as cardiovascular, renal, and neuropathic diseases.
2. How Does Diet Management Help in Type 2 Diabetes?
Diet management helps in controlling blood sugar levels, decreases the body’s resistance to insulin and helps keep in appropriate weight. Eating the right foods in the right proportions helps in meals and does not increase blood sugar levels and lowers the chances of complications due to diabetes.
3. Which Carbohydrates Should Be Consumed or Avoided?
Take complex low glycaemic carbohydrates such as whole grain, vegetables and legumes. Steer clear of simple sugars carried out by sweetened products, white bread and confectioneries since they lead to a quick rise in blood sugar levels.
4. What Types of Fats Are Recommended for Managing Type 2 Diabetes?
Saturated fat intake is discouraged, however, unsaturated fat such as mono and poly unsaturated fats are encouraged. This includes olive oils, avocados, nuts, salmon, and other oilier fishes. These types of fats control risk factors for heart diseases and also lower bad lipids in blood.
5. Why are lean proteins essential in a Type 2 Diabetes diet?
Lean cuts of meat such as chicken breast, fish, tofu and beans can slow down the digestion of carbohydrates which in turn keeps blood sugar levels in control. They assist in muscle growth and repair without risking a lot of fat accumulation, hence better management of glucose.
6. How does higher intake of fiber help those with Type 2 Diabetes?
Fiber decreases the rate of glucose absorption hence preventing any surge in blood sugar level and also helps in effective management of weight. Too many high-fiber foods such as fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains highlight the health of the digestive tract and lower the chances of getting heart diseases.
7. What Foods are Recommended and Recommended Against When it Comes to Type 2 Diabetes Diet?
Recommended: All non-starchy vegetables, whole grains (not white rice), lean protein (in reasonable portions), healthy fats, low-fat dairy (including yogurt), and fruit in small portions.
Recommended Against or Limited: Non-diet sodas and juices, mostly fatty and fried foods, sugar assorted food items, white bread and its products, and all types of meat to keep blood sugar levels steady within the working limits.
8. Physical Exercise Interventions in Type 2 Diabetes Management. How is it helpful?
In addition, physical activity on a regular basis encourages better sensitivity to insulin, controls weight, decreases anxiety levels, and cardiovascular fitness also improves. Such activities include walking, swimming, cycling, resistance training, and the like which are all helpful and should be practiced for at least 150 minutes a week.

